js对象
js对象
创建对象的几种方式
⑴ 字面量
var o1 = {name: 'o1'};
var o11 = new Object({name: 'o11'});
console.log(typeof o1); // Object
⑵ 通过构造函数
var M = function(name){this.name = name};
var o2 = new M('o2');
⑶ Object.create
var P = {name: 'o3'};
var o3 = Object.create(P);
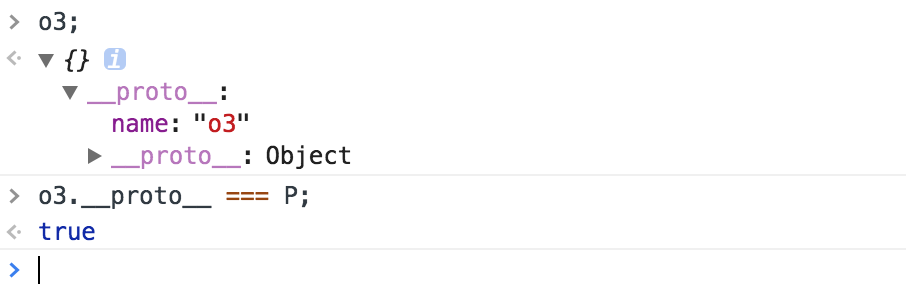
使用Object.create()是将对象继承到__proto__属性上
var test = Object.create({x:123,y:345});
console.log(test);//{__proto__: {x:123,y:345}}
console.log(test.x);//123
console.log(test.__proto__.x);//3
console.log(test.__proto__.x === test.x);//true
对象分类-classify
❃ 普通对象:有__proto__属性(指向其原型链),没有prototype属性。
❃ 原型对象:原型对象(Person.prototype)是 构造函数(Person)的一个实例。(Person.prototype 原型对象还有constructor属性,指向构造函数对象)
❃ (构造)函数对象:凡是通过new Function()创建的都是构造函数对象。拥有__proto__、prototype属性(指向原型对象)。
- Function、Object、Array、Date、String、自定义函数
- 特例: Function.prototype 是原型对象,却是函数对象
在 Person 创建的时候,创建了一个它的实例对象并赋值给它的 prototype
// 原型对象
var A = new Person();
Person.prototype = A;
函数对象
function f1(){};
var f2 = function(){};
var f3 = new Function('str','console.log(str)');
console.log(typeof f1); //function
console.log(typeof f2); //function
console.log(typeof f3); //function
console.log(typeof Object); //function
console.log(typeof Array); //function
console.log(typeof String); //function
console.log(typeof Date); //function
console.log(typeof Function); //function
Function.prototype是个例外,它是原型对象,却又是函数对象,作为一个函数对象,它又没有prototype属性。
function Person(){};
console.log(typeof Person.prototype) // Object
console.log(typeof Object.prototype) // Object
console.log(typeof Function.prototype) // function 它是特殊 Function
console.log(typeof Function.prototype.prototype) //undefined 函数对象却没有prototype属性
通过 new Function( ) 产生的对象都是函数对象。因为 A 是函数对象,所以Function.prototype 是函数对象。
var A = new Function ();
Function.prototype = A;
new运算符
描述 new 一个对象的过程
⑴ 创建一个新对象, 它继承了对象类型的原型,即foo.prototype
⑵ 将构造函数的作用域赋给新对象(因此this就指向了这个新对象)
⑶ 执行构造函数中的代码(为这个新对象添加属性,即对this赋值)
⑷ 返回this。如果构造函数return了一个新的“对象”,那么这个对象就会取代整个new出来的结果。如果构造函数没有return对象,那么就会返回步骤1所创建的对象,即隐式返回this。
function Foo(name, age) {
this = {};
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.class = 'class-1';
// return this; // 默认有这一行
}
var foo = new Foo('zhangsan', 20);
var foo1 = new Foo('lisi', 22); //创造多个对象
var new2 = function(func){
var o = Object.create(func.prototype);
var k = func.call(o);
if (typeof k === 'object') {
return k;
} else {
return o;
}
}
instanceof
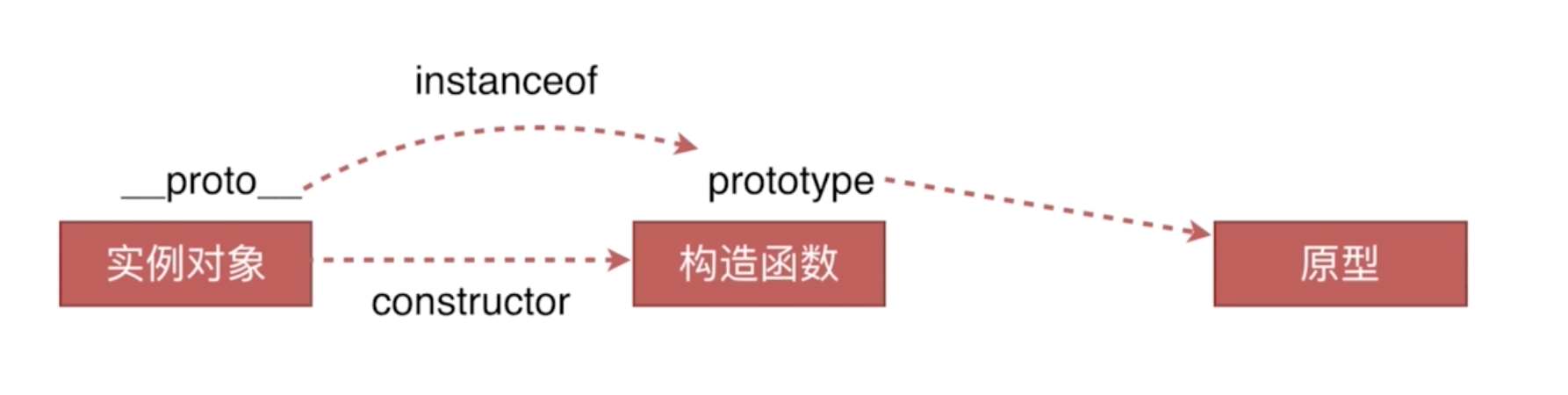
instanceof 运算符用来检测 constructor.prototype 是否存在于参数 object 的原型链上。
object instanceof constructor
object instanceof constructor 的判断逻辑是: object 的 __proto__ 一层一层往上,能否对应到constructor.prototype
㈠ 使用 instanceof 就是判断一个实例是否属于某种类型。
// 判断 foo 是否是 Foo 类的实例
function Foo(){}
var foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo instanceof Foo)//true
㈡ instanceof 可以在继承关系中用来判断一个实例是否属于它的父类型。
// 判断 foo 是否是 Foo 类的实例 , 并且是否是其父类型的实例
function Aoo(){}
function Foo(){}
Foo.prototype = new Aoo();//JavaScript 原型继承
var foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo instanceof Foo)//true
console.log(foo instanceof Aoo)//true
https://developer.mozilla.org/instanceof
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/web/1306_jiangjj_jsinstanceof/
hasOwnProperty
hasOwnProperty() 方法会返回一个布尔值,指示对象是否具有指定的属性作为自身(不继承)属性。
o = new Object();
o.prop = 'exists';
o.hasOwnProperty('prop'); // 返回 true
o.hasOwnProperty('toString'); // 返回 false
o.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty'); // 返回 false
var buz = {
fog: 'stack'
};
for (var name in buz) {
// 高级浏览器已经在 for in 中屏蔽了来自原型的属性
// 但是这里建议大家还是加上这个判断,保证程序的健壮性
if (buz.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
alert("this is fog (" + name + ") for sure. Value: " + buz[name]);
}
}
developer.mozilla.org/hasOwnProperty
类的声明与实例化-class
// 类的声明
function Animal() {
this.name = 'name';
}
// ES6中class的声明
class Animal2{
constructor() {
this.name = name;
}
}
// 实例化
console.log(new Animal(), new Animal2());