JS算法-遍历 DOM 树(深度优先、广度优先)
遍历 DOM 树
- 深度优先遍历,结果会输出什么?
- 广度优先遍历,结果会输出什么?
深度优先遍历 DOM 树
深度优先遍历输出:
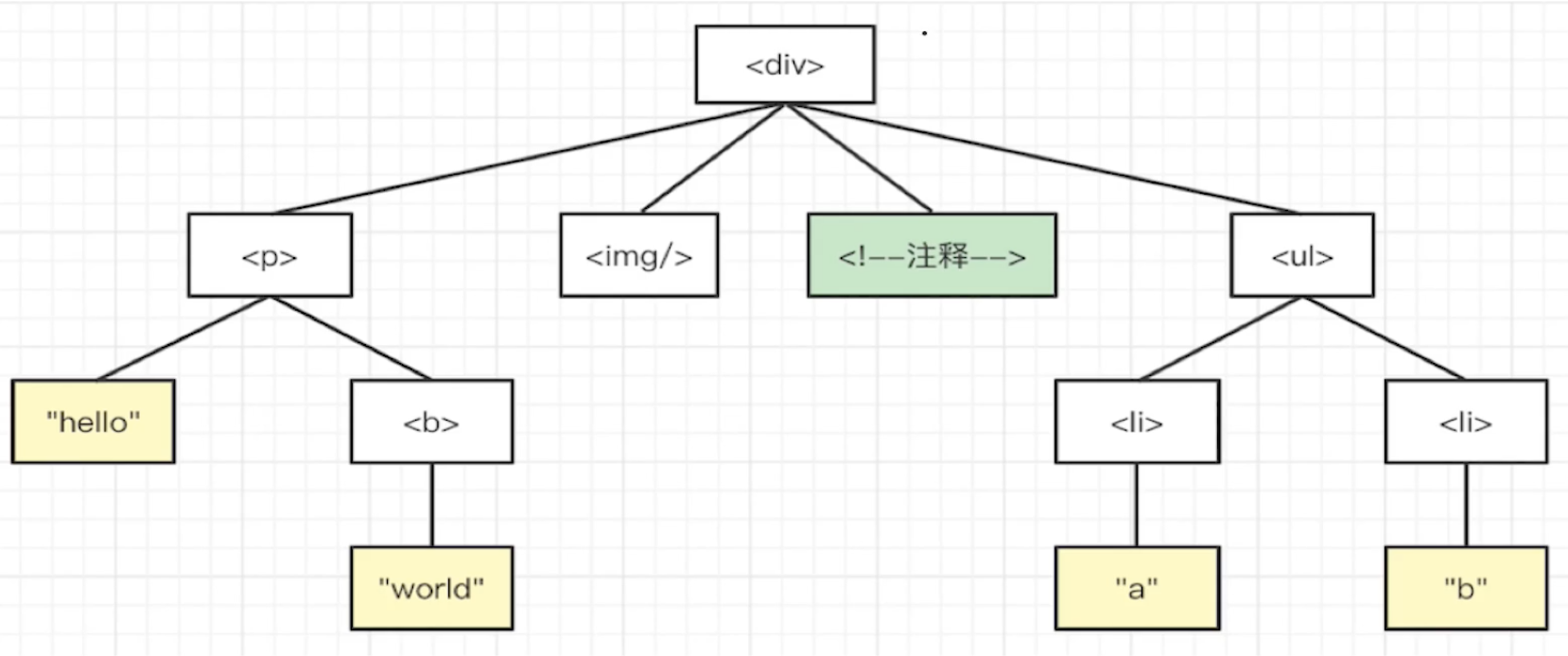
Element node--- <div>
Element node--- <p>
Text node--- hello
Element node--- <b>
Text node--- world
Element node--- <img>
Comment node--- 注释
Element node--- <ul>
Element node--- <li>
Text node--- a
Element node--- <li>
Text node--- b
用递归方法
<body>
<div id="box">
<p>hello <b>world</b></p>
<img src="" alt="">
<!--注释-->
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var root = document.getElementById('box');
function visitNode(node){
// 注释
if (node instanceof Comment) {
console.log('Comment node---',node.textContent)
}
// 文本
if (node instanceof Text) {
const t = node.textContent?.trim();
if (t) {
console.log('Text node---',t);
}
}
// element
if (node instanceof HTMLElement) {
console.log('Element node---',`<${node.tagName.toLowerCase()}>`)
}
}
function depthFirstTraverse(root) {
visitNode(root);
const childNodes = root.childNodes; // .childred 和 .childNodes 不一样
if (childNodes.length) {
childNodes.forEach(item => {
depthFirstTraverse(item) // 递归
})
}
}
console.log(depthFirstTraverse(root))
</script>
</body>
如果不用递归,可以用栈实现深度优先遍历,法二:
function depthFirstTraverse2(root) {
const stack = [];
// 根节点入栈
stack.push(root);
while(stack.length > 0) {
const curNode = stack.pop();
if (curNode == null) break;
visitNode(curNode);
// 子节点入栈
const childNodes = curNode.childNodes;
if (childNodes.length) {
Array.from(childNodes).reverse().forEach(item => {
stack.push(item)
})
}
}
}
console.log(depthFirstTraverse2(root))
广度优先遍历 DOM 树

广度优先遍历输出:
Element node--- <div>
Element node--- <p>
Element node--- <img>
Comment node--- 注释
Element node--- <ul>
Text node--- hello
Element node--- <b>
Element node--- <li>
Element node--- <li>
Text node--- world
Text node--- a
Text node--- b
广度优先遍历 DOM 树,使用数组队列,先进先出。
❶ 先创建一个空数组,用这个数组来存储所有要遍历的节点;
❷ 先存unshift()根节点;
❸ 只要数组不为空,当前节点pop()的时候,访问当前节点,然后把当前节点的子节点存入unshift()数组;
❹ 直到把所有节点都unshift()和pop()数组,数组为空时,while结束。
<body>
<div id="box">
<p>hello <b>world</b></p>
<img src="" alt="">
<!--注释-->
<ul>
<li>a</li>
<li>b</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var root = document.getElementById('box');
function visitNode(node){
// 注释
if (node instanceof Comment) {
console.log('Comment node---',node.textContent)
}
// 文本
if (node instanceof Text) {
const t = node.textContent?.trim();
if (t) {
console.log('Text node---',t);
}
}
// element
if (node instanceof HTMLElement) {
console.log('Element node---',`<${node.tagName.toLowerCase()}>`)
}
}
function breadthFirstTraverse(root) {
const queue = [];
// 根节点入队列
queue.unshift(root);
while(queue.length > 0) {
const curNode = queue.pop();
if (curNode == null) break;
visitNode(curNode);
// 子节点入队
const childNodes = curNode.childNodes;
if (childNodes.length) {
childNodes.forEach(item => {
queue.unshift(item)
})
}
}
}
console.log(breadthFirstTraverse(root))
</script>
</body>
遍历 DOM 树,方法总结:
- 深度优先,递归,贪心
- 广度优先,使用队列(数组 vs 链表)
- .children 和 childNodes 不同