js设计原则-不常使用的设计模式
Not commonly used设计模式
other不常用设计模式概述
-
创建型:原型模式
-
结构型:桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式
-
行为型:策略模式、模板方法模式、职责链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、中介者模式、访问者模式、解释器模式
原型模式-Prototype
Prototype模式-概念
-
clone自己,生成一个新对象
-
java 默认有 clone 接口,不用自己实现
-
JS 中的应用 - Object.create
Prototype模式-代码
// Object.create 用到了原型模式的思想
// 基于一个原型创建一个对象
const prototype = {
getName: function() {
return this.first + ' ' + this.last;
},
say: function() {
console.log('hello');
}
}
// 基于原型创建 x
let x = Object.create(prototype);
x.first = 'A';
x.last = 'B';
console.log(x.getName());
x.say();
// 基于原型创建 y
let x = Object.create(prototype);
x.first = 'C';
x.last = 'D';
console.log(x.getName());
x.say();
原型模式对比JS中的原型 prototype
-
prototype 可以理解为 ES6 class 的一种底层原理
-
而class是实现面向对象的基础,并不是服务于某个模式
-
若干年后 ES6 全面普及,大家可能会忽略掉 prototype
-
但是 Object.create 却是会长久存在
桥接模式-Bridge
Bridge模式-概念
-
用于把抽象化与实现化解耦
-
使二者可以独立变化
Bridge模式-代码
class ColorShape {
yellowCircle() {
console.log('yellow circle');
}
redCircle() {
console.log('red circle');
}
yellowTriangle() {
console.log('yellow triangle');
}
redTriangle() {
console.log('red triangle');
}
}
// test
let cs = new ColorShape();
cs.yellowCircle();
cs.redCircle();
cs.yellowTriangle();
cs.redTriangle();
class Color {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Shape {
constructor(name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
draw() {
console.log(`${this.color.name} ${this.name}`)
}
}
// test
let red = new Color('red');
let yellow = new Color('yellow');
let circle = new Shape('circle', red);
circle.draw();
let triangle = new Shape('triangle', yellow);
triangle.draw()
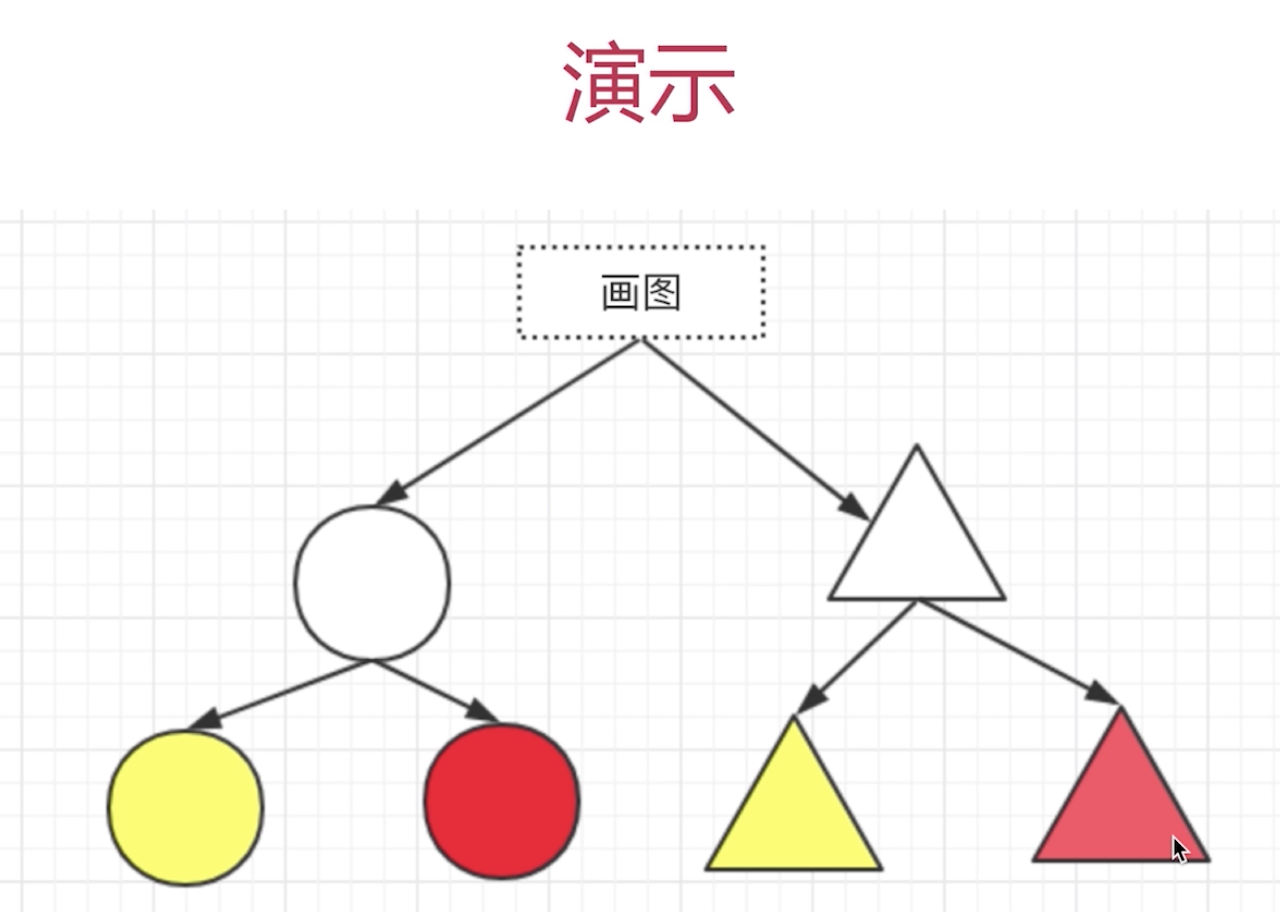
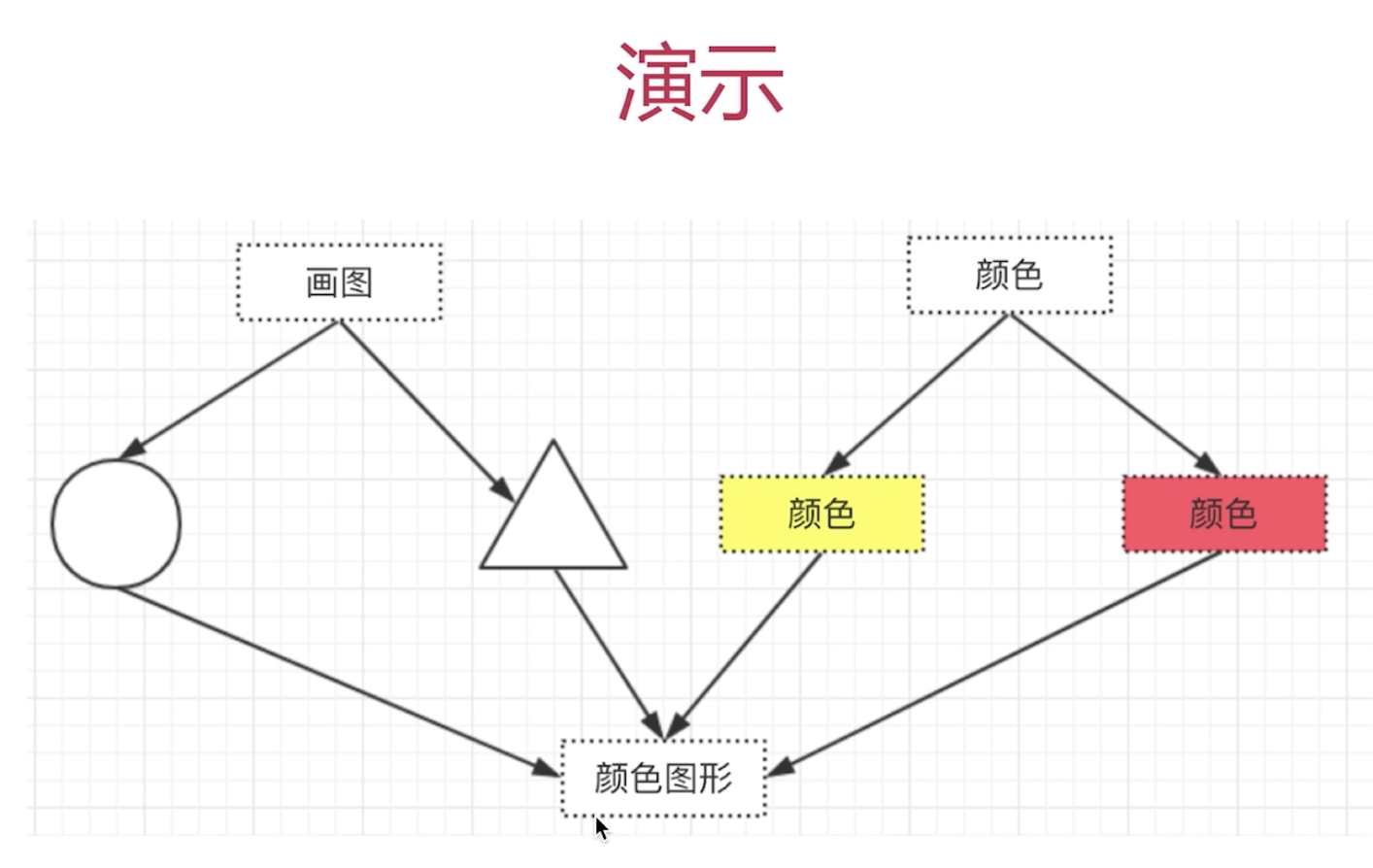
Bridge模式-设计原则验证
- 抽象和实现分离,解耦
- 符合开放封闭原则
组合模式-Composite
Composite模式-概念
-
生成树形结构,表示“整体-部分”关系
-
让整体和部分都具有一致的操作方式
Composite模式-演示
-
虚拟 DOM 中的 vnode 是这种形式,但是数据类型简单
-
用 JS实现一个菜单,不算经典应用,与业务相关
Composite模式-代码
虚拟DOM
<div id="div1" class="container">
<p><123/p>
<p>456</p>
</div>
{
tag: 'div',
attr: {
id: 'div1',
className: 'container'
},
children: [
{
tag: 'p',
attr: {},
chidren: ['123']
},
{
tag: 'p',
attr: {},
chidren: ['456']
},
]
}
- 整体和单个节点的操作是一致的
- 整体和单个节点的数据结构也保持一致
Composite模式-设计原则验证
-
将整体和单个节点的操作抽象出来
-
符合开放封闭原则
享元模式-Flyweight
Flyweight模式-概念
-
共享内存(主要考虑内存,而非效率)
-
相同的数据,共享使用
-
JS中未找到经典应用场景
Flyweight模式-代码
<!-- 无限下拉列表,将事件代理到高层节点上 -->
<!-- 如果都绑定到<a>标签,对内存开销太大 -->
<div id="div1">
<a href="#">a1</a>
<a href="#">a2</a>
<a href="#">a3</a>
<a href="#">a4</a>
<!-- 无限下拉列表 -->
</div>
<script>
var div1 = document.getElementById("div1");
div1.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
var target = e.target;
if (target.nodeName === 'A') {
alert(target.innerHTML)
}
})
</script>
Flyweight模式-设计原则验证
-
将相同的部分抽象出来
-
符合开放封闭原则
策略模式-Strategy
Strategy模式-概念
-
不同策略分开处理
-
避免出现大量 if…else… 或者 switch…case…
-
JS 中未找到经典应用场景
Strategy模式-代码
class User {
constructor(type) {
this.type = type;
}
buy() {
if (this.type === 'ordinary') {
console.log('普通用户购买');
}else if (this.type === 'member') {
console.log('会员用户购买');
}else if (this.type === 'vip') {
console.log('vip 用户购买');
}
}
}
// test
let u1 = new User('ordinary');
u1.buy()
let u2 = new User('member');
u2.buy()
let u3 = new User('vip');
u3.buy()
修改为以下的策略模式
class OrdinaryUser {
buy() {
console.log('普通用户购买');
}
}
class MemberUser {
buy() {
console.log('会员用户购买');
}
}
class VipUser {
buy() {
console.log('vip 用户购买');
}
}
// test
let u1 = new OrdinaryUser();
u1.buy()
let u2 = new MemberUser();
u2.buy()
let u3 = new VipUser();
u3.buy()
Strategy模式-设计原则验证
-
不同策略,分开处理,而不是混合在一起
-
符合开放封闭原则
模板方法模式-Template Method
class Action {
handle() {
handle1()
handle2()
handle3()
}
handle1() {
console.log('1')
}
handle2() {
console.log('2')
}
handle3() {
console.log('3')
}
}
职责链模式-Chain of Responsibility
Chain of Responsibility-概念
- 一步操作可能分为多个职责角色来完成
- 把这些角色都分开,然后用一个链串起来
- 将发起者和各个处理者进行隔离
Chain of Responsibility-演示代码
// 请假审批,需要组长审批、经理审批、最后总监审批
class Action {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.nextAction = null;
}
setNextAction(action) {
this.nextAction = action;
}
handle() {
console.log(`${this.name} 审批`)
if (this.nextAction != null) {
this.nextAction.handle()
}
}
}
let a1 = new Action('组长')
let a2 = new Action('经理')
let a3 = new Action('总监')
a1.setNextAction(a2);
a2.setNextAction(a3);
a1.handle()
-
职责链模式和业务结合较多,js中能联想到链式操作
-
jQuery 的链式操作,Promise.then 的链式操作
Chain of Responsibility-设计原则验证
-
发起者与各个处理者进行隔离
-
符合开放封闭原则
命令模式-Command
Command模式-概念
-
执行命令时,发布者和执行者分开
-
中间加入命令对象,作为中转站
Command模式-演示代码
// 触发者
class Invoker {
constructor(command) {
this.command = command;
}
invoke() {
console.log('开始');
this.command.cmd();
}
}
// 命令者
class Command {
constructor(receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
cmd() {
console.log('触发命令');
this.receiver.exec();
}
}
// 接收者
class Receiver {
exec() {
console.log('执行');
}
}
// 士兵
let soldier = new Receiver();
// 小号手
let trumpeter = new Command(soldier);
// 将军
let general = new Invoker(trumpeter);
general.invoke()
Command模式-JS 中的应用
- 网页富文本编辑器操作,浏览器封装了一个命令对象
- document.execCommand(‘bold’);
- document.execCommand(‘undo’);
Command模式-设计原则验证
- 命令对象与执行对象分开,解耦
- 符合开放封闭原则
备忘录模式-Memento
Memento模式-概念
- 随时记录一个对象的状态变化
- 随时可以恢复之前的某个状态(如撤销功能)
- 未找到JS中经典应用,除了一些工具(如编辑器)
Memento模式-演示代码
// 备忘类
class Memento {
constructor(content) {
this.content = content;
}
getContent() {
return this.content;
}
}
// 备忘列表
class CareTaker {
constructor() {
this.list = [];
}
add(memento) {
this.list.push(memento)
}
get(index) {
return this.list[index]
}
}
// 编辑器
class Editor {
constructor() {
this.content = null;
}
setContent(content) {
this.content = content;
}
getContent() {
return this.content
}
saveContentToMemento() {
return new Memento(this.content)
}
getContentFromMementent(memento) {
this.content = memento.getContent();
}
}
// test
let editor = new Editor();
let careTaker = new CareTaker();
editor.setContent('111');
editor.setContent('222');
careTaker.add(editor.saveContentToMemento()); // 存储备忘录
editor.setContent('333');
careTaker.add(editor.saveContentToMemento()); // 存储备忘录
editor.setContent('444');
console.log(editor.getContent());
editor.getContentFromMementent(careTaker.get(1)) // 撤销
console.log(editor.getContent());
editor.getContentFromMementent(careTaker.get(0)) // 撤销
console.log(editor.getContent());
Memento模式-设计原则验证
-
状态对象与使用者分开,解耦
-
符合开放封闭原则
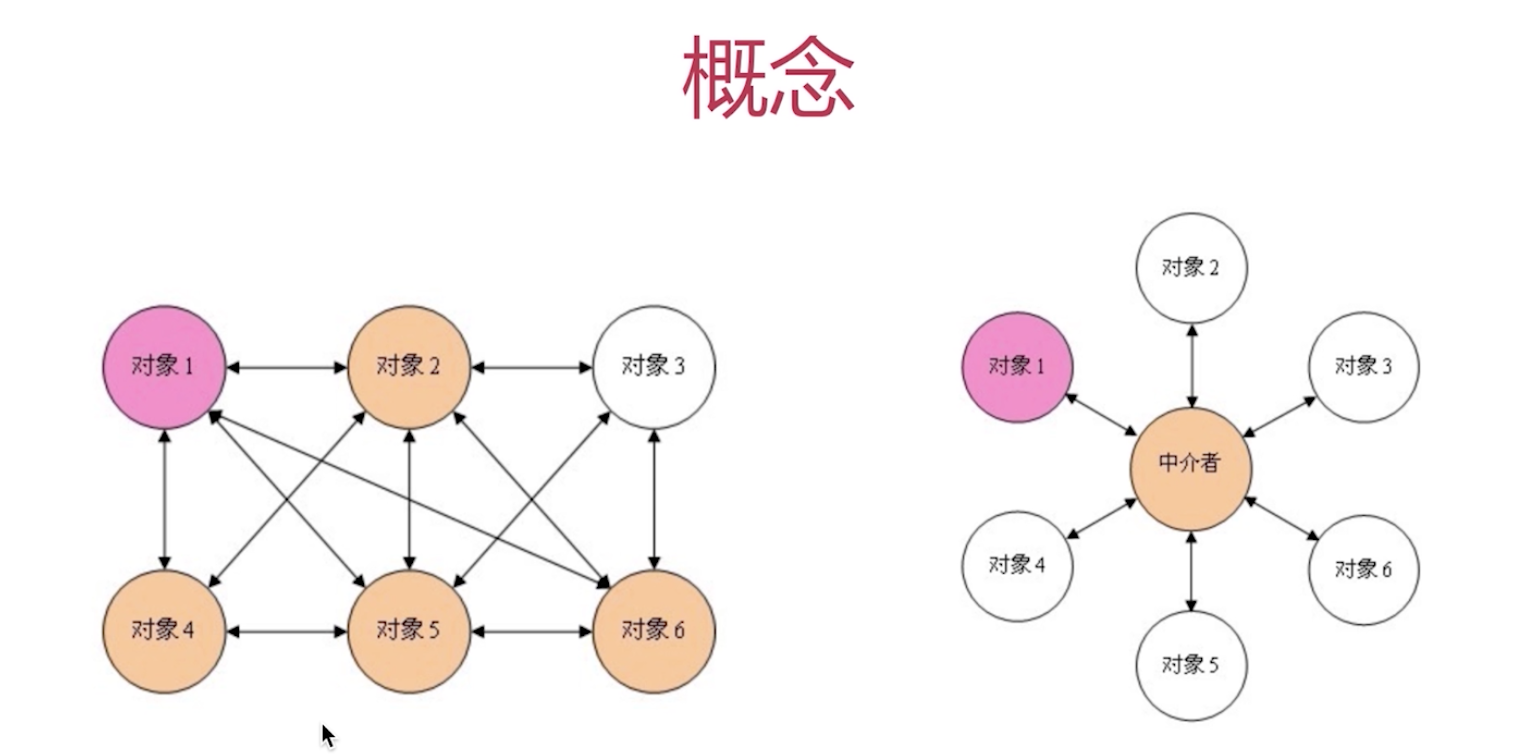
中介者模式-Mediator
Mediator模式-概念
- 类似买房、租房时中介者
Mediator模式-演示代码
class Mediator {
constructor(a, b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
setA() {
let number = this.b.number;
this.a.setNumber(number * 100);
}
setB() {
let number = this.a.number;
this.b.setNumber(number / 100);
}
}
class A {
constructor() {
this.number = 0
}
setNumber(num, m) {
this.number = num;
if (m) {
m.setB()
}
}
}
class B {
constructor() {
this.number = 0
}
setNumber(num, m) {
this.number = num;
if (m) {
m.setA()
}
}
}
let a = new A();
let b = new B();
let mediator = new Mediator(a,b);
a.setNumber(3,mediator);
mediator.setB();
console.log(b.number);
Mediator模式-设计原则验证
-
将各关联对象通过中介者隔离
-
符合开放封闭原则
访问者模式-Visitor
Visitor模式-概念
-
将数据操作和数据结构进行分离
-
使用场景极少
解释器模式-Interpreter
-
描述语言语法如何定义,如何解释和编译
-
用于专业场景,使用场景极少