js设计模式-面向对象 & UML类图介绍
js设计模式-面向对象 & UML类图介绍
OOP: Object Oriented Programming
面向对象编程
OOP概念
面向对象编程就是将你的需求抽象成一个对象,然后针对这个对象分析其特征(属性)与动作(方法)。这个对象我们称之为类。
JavaScript 是一种解释性的弱类型语言(无类语言),但是可以使用函数来模拟类。
ES5 创建对象
// 类,创建一个类
var People = function(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
People.prototype.eat = function() {
alert(`${this.name} eat something`)
}
// 创建实例
let zhang = new People('zhang', 20);
zhang.eat();
ES6 创建对象
// 类 Class,创建一个类
class People {
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
eat(){
alert(`${this.name} eat something`)
}
}
// 对象(实例),创建实例
let zhang = new People('zhang', 20);
zhang.eat();
OOP三要素:继承、封装、多态
-
继承,子类继承父类
-
封装,数据的权限和保密
-
多态,同一接口不同实现
OOP 继承
// 父类
class People {
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
speak(){
alert(`My name is ${this.name}, age ${this.age}`)
}
}
// 子类继承父类
class Student extends People {
constructor(name, age, number) {
super(name, age);
this.number = number;
}
study() {
alert(`${this.name} study`)
}
}
// 实例
let xiaoming = new Student('xiaoming', 10, 'A1');
xiaoming.study();
console.log(xiaoming.number);
xiaoming.speak();
-
People 是父类,公共的,不仅仅服务于 Student
-
继承可将公共方法抽离出来,提高复用,减少冗余
OOP 封装
-
public 完全开放
-
protected 对子类开放
-
private 对自己开放
-
(ES6尚不支持)
Javascript 是函数级作用域
var Book = function(id, name) {
// 私有属性
var num = 1;
// 私有方法
function checkId() {
}
// 特权方法
this.getNum = function() {
return num;
}
// 对象公有属性
this.id = id;
// 对象公有方法
this.copy = function() {
}
}
// 类静态公有属性(对象不能访问)
Book.isChinese = true;
// 类静态公有方法(对象不能访问)
Book.resetTime = function() {
console.log('new Time');
};
Book.prototype = {
// 公有方法
isJSBook: false,
// 公有方法
display: function(){}
}
// test
var b = new Book(11, 'js设计模式');
console.log(b.getNum()); // 1
console.log(b.num); // undefined
console.log(b.id); // 11
console.log(b.isJSBook); // false
console.log(b.isChinese); // undefined
console.log(Book.isChinese); // true
Book.resetTime(); // 'new Time'
封装优点:
-
减少耦合,不该外露的不外露
-
利于数据、接口的权限管理
-
ES6目前不支持,一般认为 _ 开头的属性都是 private
OOP 多态
-
同一个接口,不同表现
-
JS应用极少
-
需要结合Java等语言的接口、重写、重载等功能
// 多态
function add() {
var arg = arguments,
length = arg.length;
switch (length) {
case 0:
return 10;
case 1:
return 10 + arg[0];
case 2:
return arg[0] + arg[1];
}
}
console.log(add()); // 10
console.log(add(5)); // 15
console.log(add(20, 30)); // 50
-
保持子类的开放性和灵活性
-
面向接口编程
-
(JS引用极少,了解即可)
OOP js的应用举例
-
jQuery 是一个 Class
-
$(‘p’) 是jQuery 的一个实例
class jQuery {
constructor(selector){
let slice = Array.prototype.slice;
let dom = slice.call(document.querySelectorAll(selector));
let len = dom ? dom.length : 0;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
this[i] = dom[i];
}
this.length = len;
this.selector = selector || "";
}
append(node) {
}
addClass(name) {
}
html(data) {
}
// 此处省略若干API
}
window.$ = function(selector) {
// 工厂模式
return new jQuery(selector)
}
var $p = $('p');
console.log($p);
console.log($p.addClass)
OOP 的意义
为何使用面向对象?
-
程序执行:顺序、判断、循环 - 结构化
-
面向对象 - 数据结构化
-
对于计算机,结构化的才是最简单的
-
编程应该:简单&抽象
UML 类图-介绍
-
Unified Modeling Language 统一建模语言
-
类图,UML 包含很多种图,和本课相关的是类图
-
关系,主要讲解泛化和关联
-
演示,代码和类图结合
画图工具
-
MS Office Visio
-
https://www.processon.com
类图,属性、方法
| 类名 |
|---|
| + public 属性名A:类型 # protected 属性名B:类型 - private 属性名C:类型 |
| + public 方法名A(参数1,参数2): 返回值类型 # protected 方法名A(参数1,参数2): 返回值类型 - private 方法名A(参数1,参数2): 返回值类型 |
// 父类
class People {
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
eat(){
alert(`${this.name} eat something`)
}
speak(){
alert(`My name is ${this.name}, age ${this.age}`)
}
}
以上js的类图是
| People |
|---|
| + name: String + age: Number |
| + eat(): void + speak(): void |
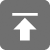
UML类图-关系
-
泛化,表示继承
-
关联,表示引用
class People {
constructor(name, house) {
this.name = name;
this.house = house;
}
saySomething() {
}
}
class A extends People {
constructor(name, house) {
super(name, house);
}
saySomething() {
alert('I am A');
}
}
class B extends People {
constructor(name, house) {
super(name, house);
}
saySomething() {
alert('I am B');
}
}
class House {
constructor(city) {
this.city = city;
}
showCity() {
alert(`house in ${this.city}`);
}
}
// 测试
let aHouse = new House('北京');
let a = new A('aaa', aHouse);
console.log(a); //a有房子
let b = new B('bbb');
console.log(b); /// b无房子